The condition placenta previa is a pregnancy complication in which placenta overlies or is proximate to the internal opening of the mother’s cervix and can cause excessive bleeding during any stage of pregnancy.

What Is Placenta Previa?
The placenta is an organ created during the pregnancy and is attached to the womb. It forms an important connection between mother and baby via the umbilical cord and provides all the essential nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. It is also responsible for removing waste products from baby’s blood.
Normally, during pregnancy placenta is implanted in the upper uterine segment but in the condition of placenta previa, the placenta is in lower uterine segment. It either covers the mother’s cervix totally or partially.
Placenta Previa In Early Pregnancy
In early pregnancy if the placenta is low then it’s quite normal because with progression of pregnancy it generally moves to the top of uterus. It is generally not considered a problem during early pregnancy as the placenta is likely to move upwards to the upper side of the uterus where there is more blood supply. Only a small percentage of pregnancies end up with a placenta previa towards the end, even though the condition is detected in early pregnancy.
During the time of labor when cervix starts opening, placenta which is lying at the bottom of uterus gets detached and severe bleeding can occur. Thus making it a dangerous condition for both mother and baby.
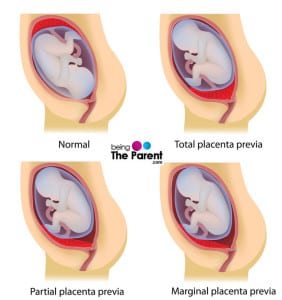
What Are They Types Of Placenta Previa?
Traditionally placenta previa is divided into four types –
- Low lying placenta:In this type placenta is extended into the lower uterine segment but does not reach the internal orifice of cervix. In most of cases it often moves upward in the uterus as the due date approaches
- Marginal placenta: When placenta just reaches the internal orifice of cervix, but does not cover it then the condition is known as marginal placenta
- Partial placenta: In this type placenta partially covers the internal orifice of cervix
- Complete placenta previa: In this the internal orifice of cervix is completely covered by placenta
Are There Any Symptoms Of Placenta Previa?
The most important symptom of placenta previa is bright red vaginal bleeding which can range between light to heavy. In most of the cases it is painless but sometimes bleeding can be accompanied with mild contractions.
In the majority of the cases bleeding usually occur either in 2nd or 3rd trimester as during that period uterus gets large and starts getting thin in order to accommodate the growing baby. Due to thinning in lower uterine segment, the placenta, which is attached at lower part of uterus gets separated.
What Are The Causes Of Placenta Previa During Pregnancy?
It is still unclear why some placentas attach themselves in the lower uterine segment but still there are some proposed factors which put you at increased risk.
- If you have uterine scarring may be because of previous surgeries, like a D&C or fibroid removal
- If your age is above 35
- If you are having multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets)
- If you are still smoking or using drugs during pregnancy
- If you have had more C-sections – the higher the number of C-sections you have had, the greater the risk
Most of the time the placenta grows wherever embryo plants itself in the uterus, so if the embryo implants in lower uterine segment then a placenta previa condition is likely to occur.
What Are The Complications Of Placenta Previa In Pregnancy?
- Bleeding: The major complication which can occur in placenta previa is severe bleeding which is a life threatening danger and can lead to hemorrhage, shock or even death.
- Pre-term baby: The other complication is pre-term delivery, due to severe bleeding an emergency C-section can occur before your full term.
- Placenta accrete: One more complication which can arise is placenta accrete. In this the placenta attaches itself too deeply in the uterine wall and then detaching it becomes a serious problem and most of the time it leads to hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). The cases of placenta accrete are increasing due to rise in the number of prior C-sections.

Diagnosis Of Placenta Previa
Placenta previa is generally diagnosed with routine ultrasound during the second trimester. Or it can also be diagnosed when pregnant women experience a vaginal bleeding and ultrasound is done to know the cause.
When placenta previa is diagnosed in second trimester a treatment may not be necessary. Especially if placenta is just touching the internal orifice of cervix then expansion of uterus can pull the attachment at higher level and it can auto correct itself without any treatment. You just need to be cautious, usually sexual inter-course and physical activities are restricted.
Treatment Of Placenta Previa
During this period treatment generally aims towards prolonging pregnancy and easing symptoms. Few of the options to ease symptoms are –
- Bed rest or if necessary short term hospitalization
- Regular monitoring of fetal heart rate and mothers vitals
- Avoiding any physical activity that can trigger uterine contraction or irritate cervix like sexual intercourse
- Mostly the treatment will depend upon how far along you are in pregnancy and condition of your and your baby’s health
The main goal will always be to keep you pregnant as long as possible. At any stage of pregnancy, a c-section may be necessary if you suffer from heavy bleeding or if you and your baby have some other dangerous problems. Depending upon the type of placenta previa , like if it is marginal placenta then may be vaginal delivery can be considered but it will always pose a threat so your doctor can suggest you a C-section. A c-section will also rule out any In case of complete placenta previa there is no option of vaginal delivery and only solution left is c-section.
In cases of heavier bleeding you can also be hospitalized and an emergency c- section can be done. In some cases women can be kept under high observation to let the baby develop a few more days.
Placenta Previa In Late Pregnancy
Most of the time complications arises when placenta previa is still present in later stage of pregnancy and bleeding occurs. In case of light bleeding a bed rest must be suggested to you with the restriction of any heavy physical activities and it can be possible that your doctor will monitor its development with regular ultrasounds. If your pregnancy has not yet reached 34 weeks, corticosteroids to speed up your baby’s lung development could be prescribed. It will also help tackle other problems related with a premature delivery.
If your pregnancy progresses without much bleeding, a planned C-section will likely be carried out in the 37th week or so. This decision will be made by your team of doctors weighing the risks and other factors.
At any stage of pregnancy you are diagnosed with placenta previa then don’t panic, just remember that it is not a disease of placenta but it is merely position of the organ that has moved from its normal position. There is no treatment to cure it and can only be stabilized. So you need to be cautious and have to take extra care.