All About Insulin During Pregnancy
6 min readWritten by Editorial Team

Diabetes is an issue that complicates any pregnancy. It can be either preexisting or gestational. If you belong to any of this category, depending on the severity and inability to keep the blood sugar within the normal range, the doctor might prescribe insulin. If you have been prescribed Insulin during your pregnancy and are uncertain about its safety, continue reading to know more about the uses and side effects of insulin during pregnancy.
Remember, keeping a strict control of blood glucose levels during pregnancy is very important in having a healthy pregnancy in women diagnosed with diabetes.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition in which the body cannot make enough insulin or is unable to use the insulin produced by the body. There are three types of diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes: A condition in which the pancreas produce little or no insulin. This is because the body’s immune system impairs the cells in the pancreas that make insulin
- Type 2 diabetes: This happens when the body either does not produce sufficient insulin or is unable to utilize the insulin produced by the body as a result developing insulin resistance
- Gestational diabetes: It is a type of diabetes that affects pregnant women. The pregnant woman does not suffer from diabetes before pregnancy. Though there are chances of developing type two diabetes in the future, more often this type of diabetes goes away after delivery
What Is Insulin?
The sugar from the carbohydrates derived from the food we eat, gets into the blood stream and is transported through the body in form of glucose. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas and it helps the body to absorb glucose from the blood. If the amount of insulin is too low, the body cannot absorb glucose. The body depends on the fat deposit for energy. This results in increased blood sugar level (hyperglycemia). If the amount of insulin increases abnormally, more glucose is absorbed from the blood resulting in too low blood sugar level (hypoglycemia). Neither of these is favorable during pregnancy and is risky for both mother and baby.
When Are Insulin Shots Recommended During Pregnancy?
If you develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy and your blood glucose levels remain high in spite of controlling diet and practicing exercises, insulin shots are prescribed. It helps to regulate blood glucose levels in order to keep the mother and baby healthy. The type of insulin and the dosage is based on:
- Recent blood sugar levels (blood sugar levels are regularly monitored)
- Mother’s diet
- How far the pregnancy has progressed
- Mother’s weight
Insulin shots are administered into the fatty tissue under the skin mostly on stomach,thigh or upper arm.
How To Take Insulin Shots During Pregnancy?
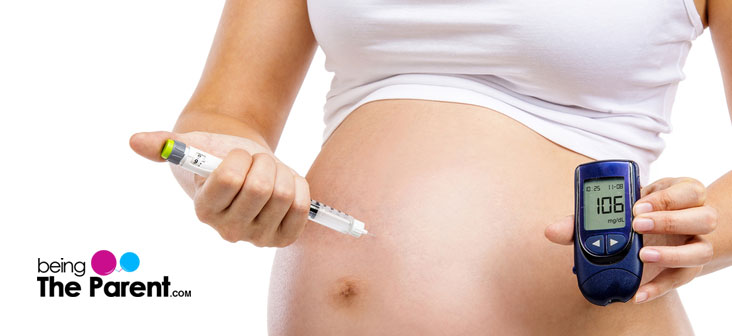
If your doctor has prescribed you insulin, you will need to inject it 1 or more times in a day depending upon the blood sugar level. Insulin is injected into fatty tissue under the skin like your belly or abdomen, upper arm or thigh. Relax and be assured that it does not cross the placenta. So in any way it will not affect your baby. Your doctor will teach you how to give yourself a shot. You’ll also get comfortable taking it yourself with practice. Check with your doctor as where to give yourself a shot. Here are some steps you can follow while injecting yourself with insulin:
- Choose the area where you want to take an insulin shot
- Prepare by cleaning the area with alcohol
- Pinch a fold of skin. Select an angle that you find easier to give yourself the insulin shot
- Keeping the skin pinched, inject the insulin by pushing the plunger down
- Release the pinched skin
- Slowly remove the needle from your skin
- Hold the injection site for 5 to 8 seconds. Don’t rub the injection area
- Use disposable needles and syringes. Sometimes your doctor may prescribe you an Insulin pen which is much easier to take

Finding The Right Dosage of Insulin During Pregnancy
Your doctor will work with you to find the right dosage of insulin for you. This may take some time before you settle on right dosage. That’s because you need to balance your insulin with your food and exercise. Your body’s need for insulin will also go up as the baby will grow. Also you will be required to check your blood sugar several times a day. This will be done to make sure your insulin is working effectively. If your blood sugar is too high or too low, your doctor will adjust your insulin dosage accordingly.
If you have type 2 diabetes before pregnancy, the insulin requirement rises considerably through each trimester
- As carbohydrate intolerance is associated with the type 2 diabetes, you will be asked to limit the intake of carbohydrates
- You will be regularly monitored and the insulin dosage will be adjusted accordingly
If you have type 1 diabetes before pregnancy, the insulin requirement fluctuates throughout pregnancy.
- You will be very closely monitored and will be required to check the glucose level 8 to 10 times every day. Before and after the meal, before bedtime and early morning
- The insulin requirement increases with the progesterone level
- During the early weeks of pregnancy, when the progesterone level will increase, insulin requirement will also go up
- After the first month of pregnancy, the level progressively increases until 10 to 12 weeks till the time the placenta takes over the progesterone production from the ovary. During this time, there will be a temporary fall in progesterone level and as a result insulin requirement will also drop
- A pregnant woman is frequently monitored throughout this period and reduced dosage of insulin is instructed. This lasts for around 8 days, after which the progesterone level again increases and as a result the insulin dosage goes up
Tips For Taking Insulin Shots Effectively During Pregnancy
- Have the right dose of insulin, especially if you are taking two types of insulin in the same syringe
- Practice how to take your shot
- Try to take the shot at same time every day
- Store the insulin as instructed so that it is effective every time you take a shot
- Always maintain a record of type and dosage of insulin administered
- For any kind of discomfort, consult your doctor immediately
- Never alter your exercise plan, diet and the dosage of the insulin without consulting the doctor
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels When Taking Insulin During Pregnancy?
You will be required to constantly monitor your blood sugar levels while taking an insulin shot to keep a check on whether your levels are in normal range or not and insulin is effective. Here is how to monitor blood glucose levels while taking insulin shot during pregnancy at home:
- You will require a glucometer to monitor blood sugar levels at home
- The glucometer comes with a small sharp needle which can be used to prick your finger tip and draw blood
- You will be required to put a drop of blood on a test strip which will be inserted in the glucometer
- After 15-20 seconds, the glucometer will flash the blood glucose result
- You need to note these results in a journal
- Remember to dispose of the needle and the strip
This way you can keep a check on your blood glucose levels at home and mention the readings to your doctor when you visit her next time
What Are The Side Effect Of Insulin During Pregnancy?
You will be asked to take the insulin shots during pregnancy only if the blood sugar levels are not controlled through diet and exercise. Regularly monitoring the sugar levels and adjusting the insulin dosage helps to minimize the side effects. However, any discomfort should not be neglected. Watch out for the following signs and contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of them.
- Feeling dizzy
- Shaking
- Tingling sensation around lips and tongue
- Racing heart
- Swelling in the face
- Sweating
- Puffiness in lips, tongue and throat
- If you have type 1 diabetes and during the first trimester, when the progesterone level drops, if the insulin dosage is not adjusted accordingly, there are higher chances of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
So, regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels is vital to know the effectiveness of insulin and to regulate its dosage from time to time during pregnancy. Do talk to your doctor about the necessary precautions and tests.

Editorial Team,
With a rich experience in pregnancy and parenting, our team of experts create insightful, well-curated, and easy-to-read content for our to-be-parents and parents at all stages of parenting.Read more.
Responses (0)
Want curated content sharply tailored for your exact stage of parenting?
Related articles

Butterfly Exercises to Induce Labor and Easy Childbirth
Occiput Posterior Position – Causes, Complications and Prevention

Top 200 Kannada Baby Boys Names With Meanings

Prenatal Yoga Classes – What is it And How Does it Help During Pregnancy?

Crying During Pregnancy – Does It Affect the Unborn Baby and Tips to Cope
E Coli During pregnancy – Will it Affect?
Sponsored content
Discover great local businesses around you for your kids.
Get regular updates, great recommendations and other right stuff at the right time.